LunarBot Hardware Assembling and Debugging Manual
Overview
This manual provides guidance for assembling and debugging the LunarBot hardware system. It covers wheel-servo connections, power systems, computation module setup, and network configuration.
(1) Wheel to Servo Connection
Required Components
- Chassis body with wheels
- Electro board with servos
- Power cables (U, V, W, PE)
- Sensor cables (24V⁺, 24V⁻/GND)
- Signal cable
Connection Steps
- Connect all power cables from motors to corresponding servos following labels on the servo
- Connect all 24V⁺ cables to the powering module on the electro board
- Connect all 24V⁻ cables to the same GND relative to each steering servo's 24V⁺
- Plug signal cables for origin and limitation sensors into "signal-in" slots on driving servos
Important Notes
- Configure proper signal-in slots in Kinco software for the servo driver
- Ensure all connections are secure before powering on
(2) Servo to Computation Module Connection
Connection Setup
- Connect all servos in series using RJ45 cables from "in" to "out" ports
- Connect the last servo in the series to the computation module
- Use a certified RJ45 extractor to get CAN_H and CAN_L lines
- Connect through a USB-CAN converter
Configuration
After physical connections, setup CAN ports by running:
sudo ip link set can0 txqueuelen 1000
sudo ip link set can0 up type can bitrate 500000
Note: Replace "can0" with your actual device name and use the correct bitrate.
Critical Attention Points
(3) Power System Debugging
Common Issues
- Wheel not rotating smoothly
- Servos powering off automatically after startup
Solutions
- Check battery capacity (do not rely solely on capacity indicator)
- Ensure proper voltage levels (24V minimum)
- Verify all power connections are secure
(4) Robot Manipulator and Gripper
Connections
- Connect manipulator to low-voltage power cell (24V, 100W minimum) using 2-wire aeroplane cable
- Connect RJ45 cable to computation module for communication
- Connect gripper to link 7 (frange) of manipulator using 5-wire aeroplane cable
See docs/Manipulator and Gripper.md for usage and important notes about manipulator and gripper.
(5) Computation Module Setup
Network Configuration
Determine Network Manager
cat /etc/netplan/*.yaml
If YAML is not empty, NetPlan is managing networks. Otherwise, NetworkManager is likely in use.
Check Network Status
nmcli device status
Disable Internal Wifi Card
- Identify internal WiFi card name (unplug external card and run ifconfig)
- Assume internal card name is wlpaaaa with connection Tsinghua-Secure
- Disable using:
sudo nmcli connection modify "Tsinghua-Secure" autoconnect no
sudo nmcli device down "wlpaaaa"
Verify Disabled Connection
nmcli connection status
Ethernet Connection with Realman Robot Manipulator
As the manipulator is connected to the NUC via Ethernet, you need to configure the Ethernet connection manually to avoid conflict with the wifi connection.
- Configure the ip address by Ubuntu Setteings->Network->Wired->IPV4 Settings->Manual. and set the ip address to
192.168.1.100, subnet mask to255.255.255.0, and gateway to192.168.1.1.
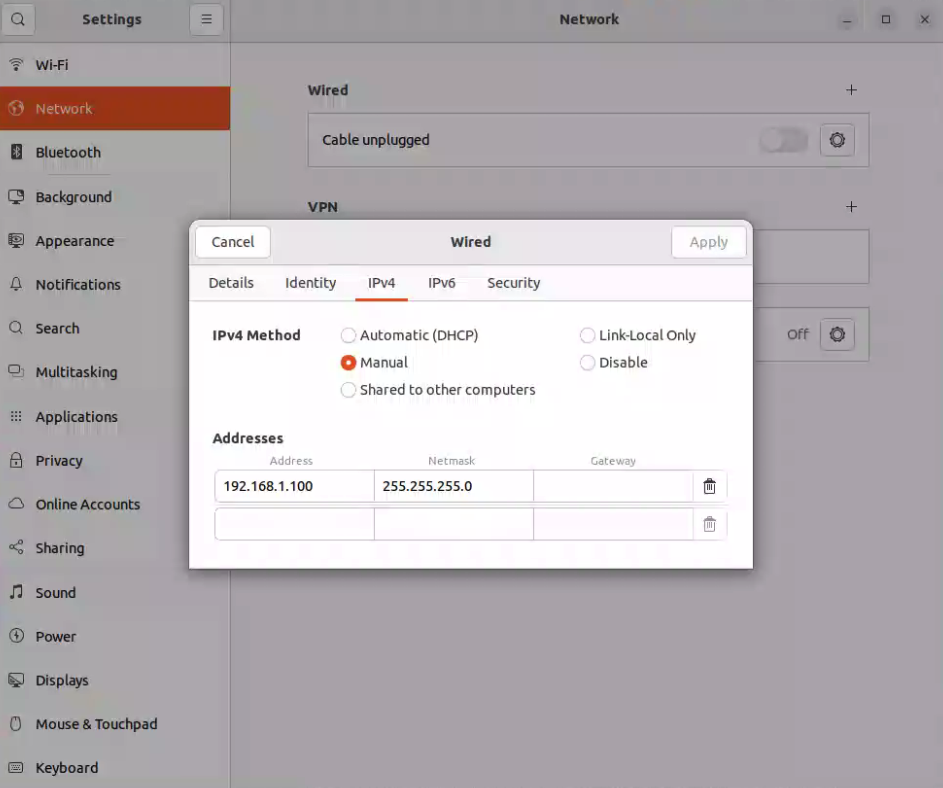
- Configure Static IP for the Ethernet Interface and make sure ethernet is NOT the default connection.
nmcli connection modify "Wired-Connection-1" ipv4.addresses 192.168.1.100/24 ipv4.method manual
nmcli connection modify "Wired-Connection-1" ipv4.gateway ""
- Configure WiFi for General Network Traffic.
nmcli connection modify "WiFi-Connection-1" ipv4.method auto
- Configure the Ethernet connection to manipulator and turn on the connection.
nmcli connection modify "ethernet interface name" +ipv4.routes "192.168.1.0/24 192.168.1.1"
nmcli connection up "ethernet interface name"
(6) Safety Precautions
- Always power off the system before making connections
- Double-check all cable orientations before applying power
- Ensure proper grounding of all components
- Verify voltage levels before connecting sensitive components
(7) Troubleshooting
- If servos behave erratically, check CAN bus connections and termination
- If network conflicts occur, verify internal WiFi is disabled
- If power issues persist, test with a known-good power supply
- Refer to component-specific documentation for detailed troubleshooting
(8) Support
For additional assistance, consult:
- Kinco servo documentation
- Realman manipulator manual
- Ubuntu network configuration guides
- CAN bus implementation references